Maxillary cysts or Maxillary Sinus Retention Cysts are rounded, dome-shaped, soft tissues developed from the mucosa within the maxillary sinus. The cyst can evolve without any symptoms and generally diagnosed by several imaging exams by professionals.
This cyst is supported by fibrous connective tissue and seemed to be filled by liquid, air, or solid content regardless of its origin.
The role of CT scan imaging is very important for these cases since it reveals the rare peripheral presentation of cysts.
Radicular Cyst
Radicular cysts are generally seen in the anterior region of the jaw caused due to trauma. The development rate of this cyst is low, and severity affects adjacent teeth and roots, causing more open to the bones.
Maxillary Residual Cyst
Maxillary Residual cyst is the retention of a radicular cyst that occurs due to improper removal of radicular or other inflammatory cysts or due to the presence of ruining remnants around the tissues of teeth.
Maxillary Residual Cyst removal - the story of Kanaga
[caption id="attachment_1011" align="alignnone" width="794"]
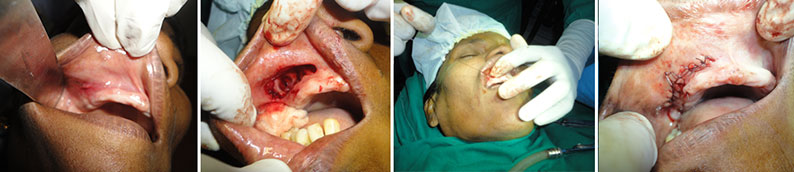
Maxillary cyst removal stages for a patient at Jerush dental and facial corrective centre, Thuckalay, Tamilnadu[/caption]
A 36-year-old female patient
Kanaga(name changed) reported to
Jerush dental and facial corrective centre, Thuckalay, Tamilnadu, with a chief complaint of slowly progressing swelling with low pain on the maxillary right front region since 2 months duration.
[caption id="attachment_1014" align="alignleft" width="150"]
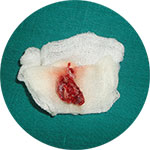
Maxillary cyst-Surgically removed pus like material[/caption]
According to the patient, the swelling was gradually increasing and there was no pus or bleeding discharge. The patient had a history of tooth extraction in the same area about 7 years ago following an accident with facial injuries.
The surgical removal of the
cyst was carried out under local anesthesia and strict asepsis through an intraoral approach. The sectioned gross specimen disclosed yellowishly, solidified pus-like material covered by a thin-layered soft capsule. Now we are glad to hear that Kanaga is totally recovered.
 Maxillary cyst removal stages for a patient at Jerush dental and facial corrective centre, Thuckalay, Tamilnadu[/caption]
A 36-year-old female patient Kanaga(name changed) reported to Jerush dental and facial corrective centre, Thuckalay, Tamilnadu, with a chief complaint of slowly progressing swelling with low pain on the maxillary right front region since 2 months duration.
[caption id="attachment_1014" align="alignleft" width="150"]
Maxillary cyst removal stages for a patient at Jerush dental and facial corrective centre, Thuckalay, Tamilnadu[/caption]
A 36-year-old female patient Kanaga(name changed) reported to Jerush dental and facial corrective centre, Thuckalay, Tamilnadu, with a chief complaint of slowly progressing swelling with low pain on the maxillary right front region since 2 months duration.
[caption id="attachment_1014" align="alignleft" width="150"] Maxillary cyst-Surgically removed pus like material[/caption]
According to the patient, the swelling was gradually increasing and there was no pus or bleeding discharge. The patient had a history of tooth extraction in the same area about 7 years ago following an accident with facial injuries.
The surgical removal of the cyst was carried out under local anesthesia and strict asepsis through an intraoral approach. The sectioned gross specimen disclosed yellowishly, solidified pus-like material covered by a thin-layered soft capsule. Now we are glad to hear that Kanaga is totally recovered.
Maxillary cyst-Surgically removed pus like material[/caption]
According to the patient, the swelling was gradually increasing and there was no pus or bleeding discharge. The patient had a history of tooth extraction in the same area about 7 years ago following an accident with facial injuries.
The surgical removal of the cyst was carried out under local anesthesia and strict asepsis through an intraoral approach. The sectioned gross specimen disclosed yellowishly, solidified pus-like material covered by a thin-layered soft capsule. Now we are glad to hear that Kanaga is totally recovered. 
No Comments yet!